Fact 4
Prebiotic forces cannot create a basic cell by arranging the four basic building blocks.
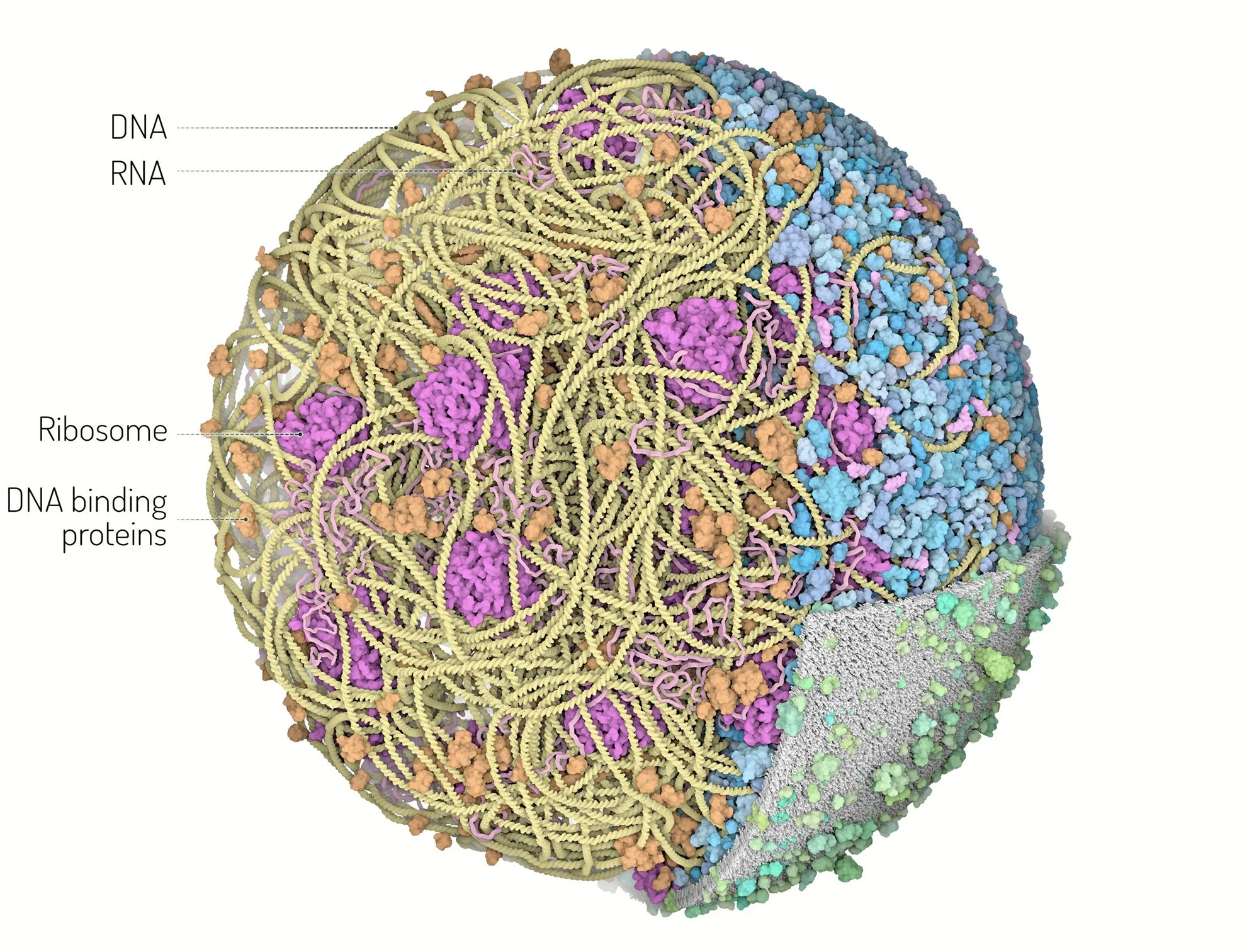
DNA and its stored information/data is useless by itself. DNA must be in a living cell that can retrieve and transmit the data through RNA to produce proteins.
Credit: Martina Maritan, Scripps Research
Make the Simplest Cells - 4 Building Blocks
Nobody has made any of the higher-order structures needed for the simplest of cells
Requirements for the simplest form of life, single cell bacteria
"This minimal gene set included genes for:
"DNA replication, repair, restriction, and modification;
"a basic transcription machinery;
"aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis;
"tRNA maturation and modification;
"ribosomal proteins;
"ribosome function, maturation, and modification;
"translation factors;
"RNA degradation;
"protein processing, folding, and secretion;
"cellular division; transport;
"and energetic and intermediary metabolism (glycolysis, proton motive force generation, pentose phosphate pathway, lipid metabolism, and biosynthesis of nucleotides and cofactors).
"Those authors did not include rRNA or tRNA genes, and they recognized that the basic substrate transport machinery could not be clearly defined, even though this minimal cell would rely greatly on the import of several substrates, including all 20 amino acids (for which it had no biosynthetic ability)."
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2014 Sep; 78(3): 487–509.
doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00050-13
Systems Biology Perspectives on Minimal and Simpler Cells
Joana C. Xavier⁽ᵃ,ᵇ⁾, Kiran Raosaheb Patil⁽ᵇ⁾, and Isabel Rocha⁽ᵃ⁾
PMCID: PMC4187685
PMID: 25184563
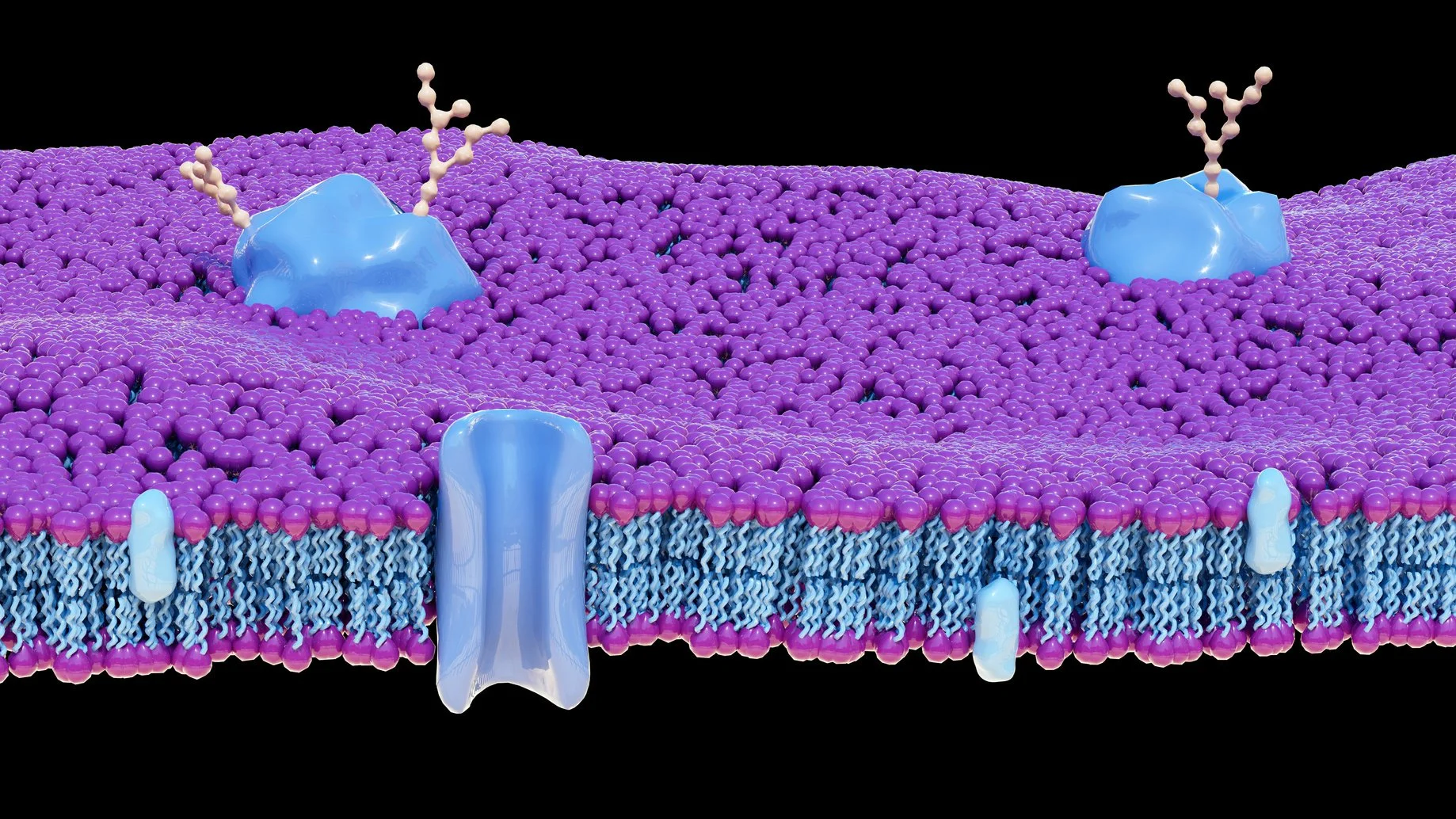
Cell Membrane
ChatGPT
The simplest known single-cell organism is Mycoplasma genitalium, a bacterium with one of the smallest genomes of any free-living organism. Here’s a quick breakdown:
Genome: It has around 580,000 base pairs and about 525 genes, which is remarkably small compared to other bacteria.
Structure: Like other bacteria, it lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. It has only the basic components needed to sustain life, such as ribosomes for protein synthesis and a plasma membrane.
Lifestyle: Mycoplasma genitalium is a parasitic bacterium that lives in host organisms, which reduces the number of genes it needs to survive because it relies on the host for many essential nutrients.
Grok 3 - 5/2/25
The simplest self-sustaining, non-parasitic single-cell organism is likely Pelagibacter ubique, a member of the SAR11 clade of bacteria. It has a small genome of about 1.3 million base pairs and roughly 1,350 genes, encoding minimal but complete metabolic pathways for independent survival in nutrient-poor ocean environments. It performs basic functions like energy production and nutrient uptake without relying on a host, making it a prime example of a free-living, self-sustaining organism with streamlined biology.
Grok3
Primary cell functions are the essential processes that cells perform to maintain life and support the organism. These functions vary by cell type but generally include:
Energy Production: Cells generate energy, primarily through cellular respiration in mitochondria, converting nutrients (e.g., glucose) into ATP to power cellular activities.
Protein Synthesis: Cells transcribe DNA into mRNA and translate it into proteins using ribosomes. Proteins serve as enzymes, structural components, or signaling molecules.
Nutrient Uptake and Waste Removal: Cells absorb nutrients (e.g., via diffusion or active transport) and expel waste products to maintain homeostasis.
Cell Division and Growth: Cells replicate through mitosis to replace damaged cells or support growth, ensuring proper development and tissue maintenance.
Communication: Cells communicate via chemical signals (e.g., hormones, neurotransmitters) or physical interactions to coordinate functions like immune responses or tissue repair.
Maintaining Homeostasis: Cells regulate internal conditions (e.g., pH, ion balance) through processes like active transport and membrane pumps. Specialized cells (e.g., neurons, muscle cells) have additional functions tailored to their roles, such as signal transmission or contraction. If you want details on a specific cell type or function, let me know!
The DNA Goal needed for life:
Organize and align 1,300,000 Nucleotides and link them together in a specific location. Then, attach nucleotide bases at a specific point and in a specific order. 1,300,000 A, T, C, and G bases or “letters” are added that need to form a coherent “message.” Then get another reciprocal strand and attach them. That’s all.
Photocell cannot be formed prebioticaly or even in a modern lab.
Episode 12.2/13: Cell Construction & Assembly Problem
Minimal Requirements for Cell Life Are Very Complex
Episode 12.2/13: Cell Construction & Assembly Problem
Rice Professor Demands Transparency on Origin of Life Chemistry
Cell Membrane Complexity
The fluid mosaic model by Singer and Nicolson in 1972 replaced the old “sandwich” idea of cell membranes. They’re not rigid barriers but flexible, protein-studded layers that control traffic—ions, nutrients, signals—revealing cells as gatekeepers with intricate communication systems.
Episode 12.2/13: Cell Construction & Assembly Problem
Cell parts need to all be randomly arranged at the same time and then somehow activated. Random non functioning parts would degrade quickly.
Build Cell Challenge
Simplest Cell
Cell Division
Summary
Photocell cannot be formed prebioticaly or even in a modern lab
Minimal requirements for cell life are very complex.
Cell Membrane Complexity
Cell parts need to all be randomly arranged at the same time and then somehow activated. Random non functioning parts would degrade quickly.
Cell construction is not all that is needed. A living cell needs to have hundreds of sensors, pathways, signals, organizers, energy, and machines to carry out the life functions of each cell.
In Fact 5, we will look at some of the amazing processes with DNA. These are only some DNA processes and does not cover all the other cell functions such as energy production, nutrient uptake and waste removal, cell division and growth, communication, and maintaining homeostasis.
Fact 5: DNA Transcription, Translation and Replication requires hundreds of complex proteins and protein machines to function.